Types of DC Motor
Separately excited DC Motor, Permanent Magnet DC Motor are some of the types of DC Motor. Read on to get to k now them in detail.
In the last blog, we learnt about the working principle of DC motor. Now, in this blog we are talking about the types of DC motor.
What is DC Motor?
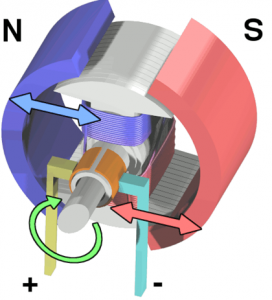
The DC motor is the motor which converts the direct current into the mechanical work. It works on the principle of Lorentz Law, which states that the current carrying conductor placed in a magnetic and electric field experience a force. To learn more about DC motors, visit Working Principle of DC motor and check out the related details.
There are two main parts of the DC motor.
- Armature
- Stator
The rotating part is armature and the Stator is their stationary part. The armature coil is connected to the DC supply.
MUST READ BLOG POSTS ON DC MOTORS
Working Principle of a DC Motor
When armature windings connect to a DC supply, an electric current sets up in the winding. Permanent magnets or field winding (electromagnetism) provides the magnetic field. In this case, current carrying armature conductors experience a force due to the magnetic field, according to the Fleming’s left hand rule.
Commutator is made segmented to achieve unidirectional torque. Otherwise, the direction of force would have reversed every time when the direction of movement of conductor is reversed in the magnetic field. This is how a DC motor works!
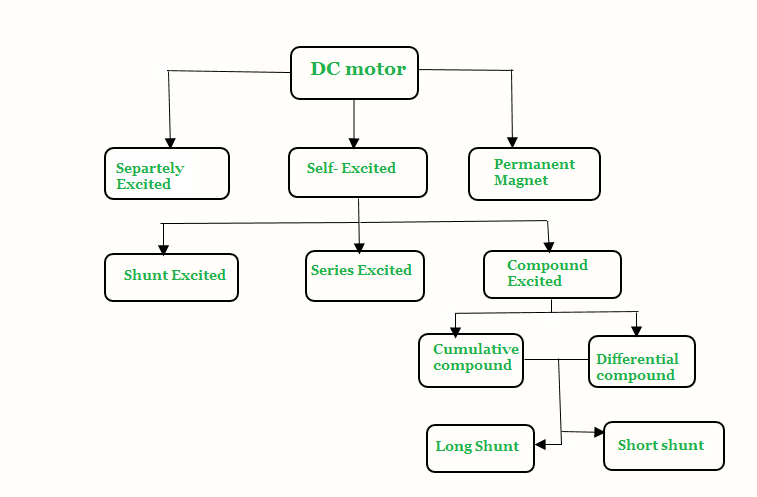
What are Different Types of DC Motor?
Understanding the different types of DC motors will also help you understand about their different applications and which type may apply to your application.
A brief chart (based on the type of construction and electrical connection) is as follow:
Now, we will discuss the various different types of DC Motors in detail.
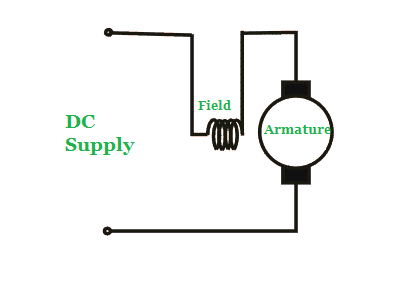
1. Separately Excited DC Motor
The separately excited DC motor requires the separate power supply to the field and armature windings. 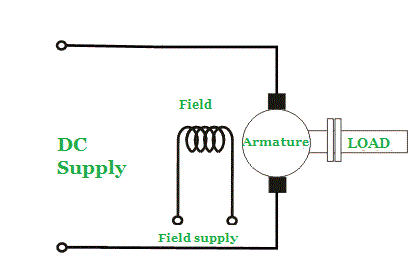
The main distinguishing fact in this type of DC motor is that, the armature current does not flow through the field windings, as the field winding energizes from a separate external source of DC current as shown in the above figure.
2. Permanent Magnet DC Motor
The permanent magnet motor uses a permanent magnet to create field flux. The construction of these types of DC motor are such that, radially magnetized permanent magnets mounted on the inner periphery of the stator core to produce the field flux.
On the other hand, the rotor has a conventional DC armature with commutator segments and brushes.
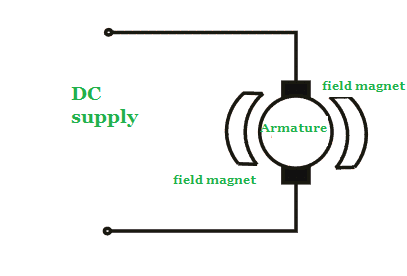 This type of DC motor provides great starting torque and has good speed regulation, but there is a limitation of torque so they are typically found on low horsepower applications.
This type of DC motor provides great starting torque and has good speed regulation, but there is a limitation of torque so they are typically found on low horsepower applications.
3. Self Excited DC motor
In case of self excited DC motor, the field winding connects either in series or in parallel or partly in series, partly in parallel to the armature winding. Based on this, self excited DC Motors can be classified as:
- Shunt wound DC motor
- Series wound DC motor
- Compound wound DC motor
a. Shunt Wound DC Motor
In shunt wound DC motors, the field is connected in parallel (shunt) with the armature windings. 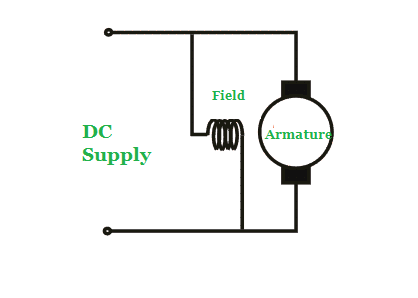
These motors offer great speed regulation due to the fact that the shunt field excited separately from the armature windings, which also offers simplified reversing controls.
b. Series Wound DC Motor
In series wound DC motor, the entire armature current flows through the field winding as it connects in series to the armature winding.
The above image shows the diagrammatically representation of the series wound DC motor. The speed of this motor varies with load and operation wise this is its main difference from a shunt wound DC motor.
c. Compound Wound DC Motor
The compound wound self excited DC motor essentially contains the field winding connected both in series and in parallel to the armature winding as shown in the figure below,
The excitation of compound wound DC motor can be of two types depending on the nature of compounding.
-
Compound DC Motor
When the shunt field flux assists the main field flux, produced by the main field connected in series to the armature winding then its called cumulative compound DC motor.
-
Differential Compound DC Motor
In case of a differential compound DC motor, the arrangement of shunt and series winding is such that the shunt field winding field flux diminishes the effect of main series field winding flux.
Both the cumulative compound and differential compound DC motor can either be of short shunt or long shunt type depending on the nature of arrangement.
Short Shunt DC Motor
In the short shunt type compound wound DC motor, the shunt field winding is only parallel to the armature winding not the series field winding.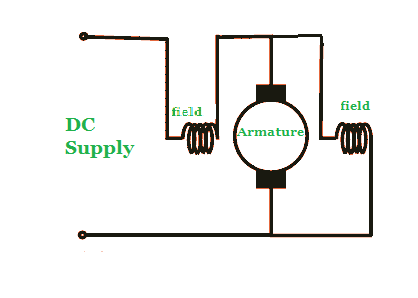
Long Shunt DC Motor
In the long shunt type compounded wound DC motor, the shunt field winding is parallel to both the armature winding and the series field winding.
Hope, this article helps you to get the brief knowledge of all the types of DC motor.
We at Robu.in hope that you found it interesting and that you will come back for more of our educational blogs.