In this article we will learn the basics of temperature sensors and their types. Also interfacing of PT100-S Temperature Sensor with Arduino UNO.

Reading temperature using Arduino sounds like a very exciting project. Because,
Temperature measurement is very common and useful in many applications. From small household to huge industrial devices everything needs to be operated within a pre-defined temperature.
You will find temperature sensor in
- Automobiles
- Computers
- Home appliances
- Medical devices
- And more….
It is responsible for maintaining the device's temperature at a rated value, thereby assuring the system's safety and long life.
In this article, we will start with the basics of temperature sensors, understand its types, and finally interfacing with Arduino.
Anyhow I will say that temperature sensor is common in engineering applications, it would help if you understand it in detail.
Table of Contents (click on the links to jump to that section)
Now without any further ado, let's start.
What is a Temperature Sensor?
It is a device that measures and converts surrounding temperature into the data that can be understood by other devices. They work on the principle of resistance or voltage change in response to temperature variations.
A temperature sensor needs to be very precise and accurate as the failure to measure temperature can lead to damage to respective as well as surrounding devices.
Types of Temperature Sensors
1. Contact Temperature Sensor

This type of temperature sensor is in direct contact with the material under observation. It works on the principle of Heat Conduction.
Useful in distinguishing solids, liquids, and gases over a broad scope of temperature.
2. Non-contact Temperature Sensor
This type of sensor helps in determining the temperature of liquids and gases that radiates energy in response to rise in heat.
It works on the principle of Convection and Radiation.
Interfacing Temperature Sensor with Arduino
We will be using PT100-S to illustrate the temperature sensor interfacing with Arduino.
What is PT100-S Temperature Sensor?
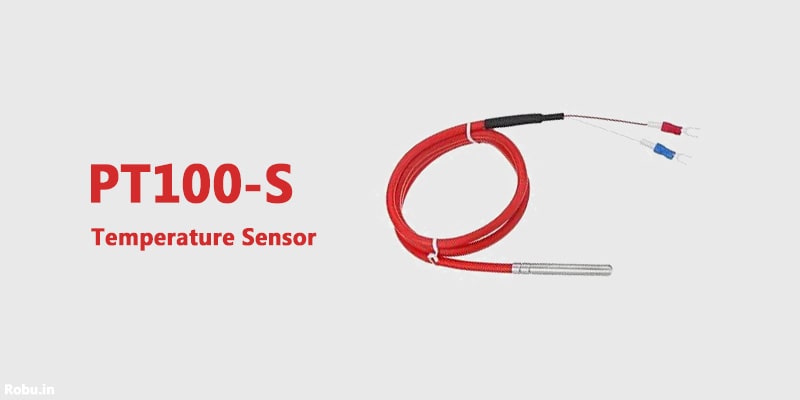
The PT100-S is a thermistor that changes the resistance value in response to the surrounding temperature changes. It has good response time, accuracy, and repeatability.
The resistor is a strip of platinum that has resistance of 100-138.4 Ω.
It is useful in laboratories and industries for measuring the temperature with excellent precision.
The PT100-S is equipped with a 316L stainless steel shield that makes it compatible with temperatures up to 420°C.
Know more about PT100-S by clicking here.
PT100-S Connection with Arduino
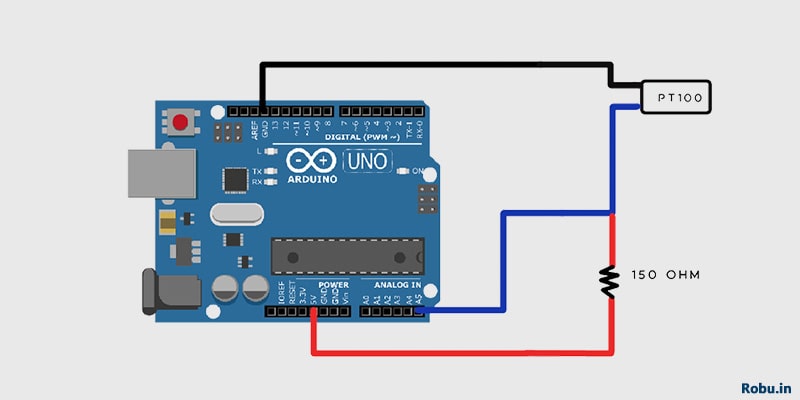
Connecting PT100-S with Arduino will take only 5-10 minutes.
Note: DO NOT connect the power supply until you ensure that everything is connected properly.
Follow the steps below to make proper connection,
Step 1 – Connect one end of the PT100-S temperature sensor to the analog pin on Arduino.
Step 2 – Now, we need to connect the same end of the sensor to 5V on Arduino through a resistor.
Resistor is added here to avoid heating problems. You can calculate value of the resistor using the formula below,
R2 = R1*1/(Vin/Vout-1)
The value of R2 should be low enough to avoid a low signal to noise ratio.
Here we are using a 150Ω resistor in this project.
Step 3 – Connect the other end of the sensor to the "GND" pin on Arduino.
Try keeping the PT100-S sensor near hot (candle) or cold (ice cube) material. You will see the change is readings.
Code
//Robu.in
#include <Wire.h>
const int analogInPin = A5; //sensor connected to A5 pin
const int SensorValueLow = 463;
const int SensorValueDiff = 36; // differance between high and low sensor value
const int TempValueDiff = 42; // differance between high and low Temp value
const int TempValueLow = 9;
int sensorValue = 0;
double Temp = 0;
void setup()
{
}
void loop()
{
sensorValue = analogRead(analogInPin);
Temp = sensorValue-SensorValueLow;
Temp = Temp/SensorValueDiff;
Temp = Temp*TempValueDiff;
Temp = Temp+TempValueLow;
Serial.print(sensorValue); //printing value of sensor on the serial monitor
Serial.print(Temp); // printing temperature on the serial monitor
delay(200); // interval of fetching data from sensor
}Conclusion
Hope this article helped you learn the basics of temperature sensor and interfacing with Arduino. If you have any doubts, then don't forget to comment below.
Also, we will love to see the prototype of your project; temperature sensor interfacing with Arduino.
Note that all of the products used in this project are available at Robu.in. Do not forget to check them as well.
Sayonara!







What is operating temperature range of non contact temperature sensor ?
Ranges between 32 to 1832°F. It also depends on the sensor you’re buying. You can check the data in the datasheet.