Photoelectric Proximity Sensor-Methods, Advantages, Applications
The blog covers the basics of photoelectric proximity sensors, its working, applications, and advantages and disadvantages.

Photoelectric proximity sensor is so versatile that it solves the bulk of problems put to industrial sensing. As photoelectric technology is so rapidly advanced, they now commonly detect targets less than 1 mm in diameter, or from 60 m away. They use in plenty of different applications and industries, often used in manufacturing and packaging. In this blog, we are talking about working Principle of Photoelectric proximity sensor.
What is Photoelectric Proximity Sensor?
Photoelectric sensors are able to detect both metallic and non-metallic targets. They uses in many applications like in mobile phones and for level sensing. In the iPhone, the sensor is used to deactivate the touch screen as the user brings the device closer to the face.
However, The main components of this sensor are emitter, detector and associated electronics. Emitter (Light Emitting Diode, laser diode) sends a beam of light. The detector (photo diode or phototransistor) detects emitted light.An associated electronics required to amplify the detected signal.
The emitter sometimes called the sender transmits a beam of either visible or infrared light to the detecting receiver.
All photoelectric sensors operate under similar principles. Dark-on and light-on classifications refer to light reception and sensor output activity. With no reception of light, the output produces then the sensor is dark-on. If output from light received then it is light-on.
Watch the video for what's coming next in this blog.
MUST READ BLOGS ON PROXIMITY SENSOR
- How proximity sensor works?
- Different types of proximity sensor
- Working principle of Inductive Proximity Sensor
- Inductive proximity sensor
- Capacitive proximity sensor
- Magnetic proximity sensor
Sensing Methods or Working Principle of Photoelectric Proximity Sensor
There are three main sensing methods of the photoelectric proximity sensor and they are,
- Through beam method
- Retro-reflective method
- Diffuse or Reflective method
Through beam method
In this type of method, an emitter sends out a beam of light directly in the line-of-sight of the emitter to a receiver. When an object breaks this beam of light, it detects as a presence. This type of setup requires two components they are an emitter and a separate detector, which makes it a bit more complex to install and wire. However, the advantage is that it’s the most accurate of the sensing methods with the longest sensing range.
New laser diode emitter models can transmit a well-collimated beam 60 m for increased accuracy and detection. At these distances, some through-beam laser sensors are capable of detecting an object the size of a fly, at close range, that becomes 0.01 mm. One ability unique to throughbeam photoelectric sensors is effective sensing in the presence of thick airborne contaminants.
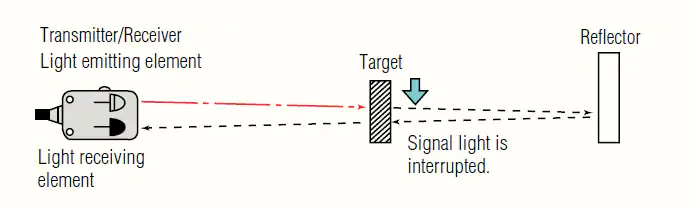
Retro-reflective method
In this method, detection occurs when the light path breaks or disturbs. Both the light emitting and light receiving elements are in same housing. The light from the emitting element hits the reflector and returns to the light receiving element. When a target is present, the light gets interrupt.
One reason for using a retro-reflective sensor over a through-beam sensor is for the convenience of one wiring location, the opposing side only requires reflector mounting.
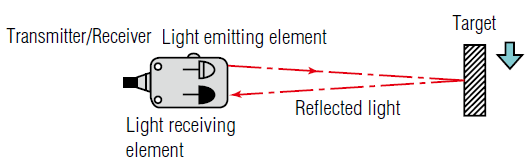
Diffuse or Reflective method
As in retro-reflective sensors, emitters and receivers located in the same housing. In this Diffuse method, Both the light emitting and light receiving elements contain in a single housing. The sensor receives the light reflected from the target.
Diffuse photoelectric sensors are similar in some respects to reflective sensors. This is because like reflective sensors they emit a light beam in the direction of the object to be detected. However, instead of a reflector used to bounce the light back to a detector, the object to be sensed functions as the reflector, bouncing some of the light back to be detected and register an object’s presence.
Mostly, the diffuse sensors use in public washroom sinks, where they control automatic faucets. Hands placed under the spray head act as reflector, triggering (in this case) the opening of a water valve. diffuse sensors are somewhat color dependent, certain versions are suitable for distinguishing dark and light targets in applications that require sorting or quality control by contrast.
Advantages of Photoelectric Proximity Sensor
- The sensor senses all kinds of materials.
- It has longer life, long sensing range and very reliability.
- Very fast response time and less costly.
- Diffuse photoelectric sensor detects small objects including color mark and label detection.
- mostly retro-reflective type sensor can detect transparent objects.
- Through beam type can detect long range and it is tolerant of dirty environment.
Disadvantages of Photoelectric Proximity Sensor
- Over coarse of time lens get contaminated.
- Generally, the sensing range is affected due to color and reflectivity of the target.
- Through beam type requires transmitter (Tx) and receiver (Rx) at two separate locations
- Retro reflective type requires reflector in addition to Tx/Rx. This makes system installation complex
Applications of Photoelectric Proximity Sensor
The photoelectric proximity sensors use in different section. Few of them are as follow,
- Checking objects on production lines or conveyors:
photoelectric sensors can detect product size to spot any errors, or simply spot their absence. As well as picking up problems like misaligned caps on bottles. They are widely used in the food and pharmaceutical industries, and in packaging plants.
- Counting of small objects:
In some production environments, small items will fall from a vibrating conveyor belt into a packaging system or bag – and a photoelectric sensor can count them.
- Detection of colours:
Through scanning independently in red, green and blue light, with applications in multiple processes in the printing and packaging sectors.
- Monitoring bigger areas for objects with light grids:
Instead of using multiple sensors, a light grid uses parallel beams of light to cover a two-dimensional area.
- Measuring distance:
With multiple sensors, a triangulation process compares reflected laser beams and can use to accurately determine position and distance. for example, to check the location of manufacturing systems, or in automated transport applications.
- Logistics and materials handling:
In an automated warehouses with robotic pickers or trucks rely on position and object sensing to operate efficiently and safely.
- Automatic doors:
In buildings or public transport, photoelectric sensors detect when someone is standing by a door.
We at Robu.in hope that you found it interesting and that you will come back for more of our educational blogs.









Hi,
Great information, thanks!
Do you possibly know of a anti collision sensor solution that can be used on large trucks in a dusty mining environment?
It should be effective at a minimum of 40 meters distance and respond to smaller vehicles as well as people which can be moving or stationary.
The trucks can also be moving or stationery.
Many thanks!