An E-bike controller is a component that connects all electrical parts on the bike together. It can manage the overall functioning of the bike.

An e-bike motor controller is one of the most important features of electric bikes. It functions as the E-bike's brain, controlling all aspects of the vehicle. To operate the E-bike, we have to connect all electrical components, like the battery, motor, throttle, brake, and sensor, to the controller. With the help of a controller, you can control the power of the motor, the speed of the bicycle, the acceleration of the bike, etc.
This article represents a guide to the e-bike motor controller. Also, here we will discuss the parameters that need to be considered while selecting the controller.
What is an E-bike motor controller?
An E-bike motor controller is a component that connects all electrical parts on the bike together. It connects things like the battery, motor, throttle, display, pedal assist, and various sensors. It is a small computer that acts as the heart of the e-bike. It can manage the overall functioning of the bike.
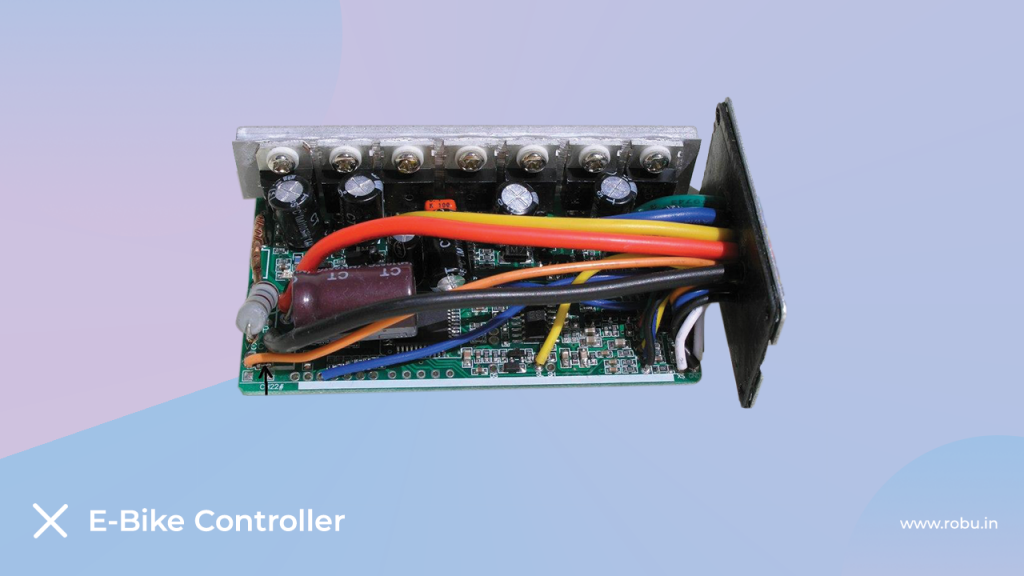

Generally, e-bike motor controllers come in a sealed protective box. The controllers can be placed open on a bicycle; however, some designs are mounted inside the frame and hidden away.
As a rule, controllers come in a sealed protective box because they are exposed to the elements. However, some designs can be mounted inside the bike’s frame and hidden away from sight.
What is the function of the e-bike controller?
The controller's main function is to take inputs from all the E-bike parts, like the throttle, battery, speed sensor, display, motor, etc., and determine what to return. The different controller design has multiple protections, which are:
- Low-voltage Protection: The controller monitors the battery voltage continuously, and it shuts down the motor whenever the voltage reaches its cut-off level. It will protect the battery against over-discharge.
- Over-voltage Protection: The controller also monitors the charge level of the battery voltage. It will automatically shut down when the battery voltage reaches its full charge.
- Over-temperature protection: The controller monitors the temperature of the FET (field-effective transistors). It will shut down the motor whenever it becomes too hot.
- Over-current Protection: If the motor takes more current, the controller reduces the current flow to the motor. It protects the motor windings as well as the FET power transistors.
- Brake Protection: The controller gives more priority to the braking signal as compared to others. For instance, if you apply the brakes and throttle simultaneously, it will perform the brake function.
Types of E-bike motor controllers
Three types of E-bike motor controllers are available: brushed DC motor controllers, brushless DC motor controllers, and BLDC motor controllers with hall sensors. Let's see these in detail.
1. Brushed DC motor controllers
Brushed DC motors come with permanent magnets to go with a connector. The design of these controllers is much simpler. It is just a set of keys that can change the current supplied to the engine.

Brushed controllers are mostly used on small electric vehicles such as scooters, electric bicycles, pedelecs, e-bikes, and other light EVs.
These controllers are pretty simple to use and are mostly used by DIY hobbyists and enthusiasts. The above image shows a set of brushed motors with controllers.
2. Brushless DC motor controllers
An E-bike, mostly BLDC motor, and BLDC controllers are used. These are brushless motors with permanent magnets. They are reliable and offer higher efficiency. The operation and service of these controllers are very simple. Generally, everything on the brushless DC motor controllers is simple, including their operation and service.

The above image shows a brushless motor with a controller. In the form of structure, it looks like the brushed controllers. Brushless controllers come with three phases controlled through a set of keys and at least two transistors (key/MOSFET) per phase. These keys are in the range of 6 (like 6, 12, 18, etc.).
3. BLDC controllers for motors with Hall Sensors
In brushed DC motors, the brushes contact the commutator and switch the current for the movement of the rotor. But there are no brushes in the BLDC motor. Thus, they need to be driven electronically using a motor control system.
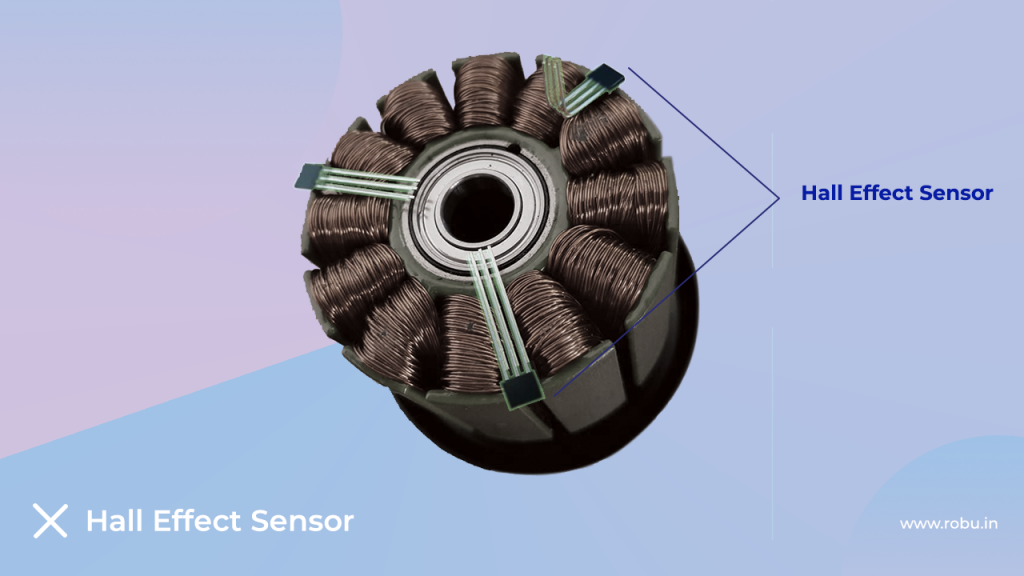
A Hall effect sensor is a transducer based on the principle of the Hall effect. Hall-effect sensors determine the position of the rotor according to the stator. The stator is the fixed part of the motor, whereas the rotor is the rotating part. It also determines the speed and various other attributes required to run a BLDC motor efficiently. These sensors, also known as rotary encoders, determine the position of the rotor.
Why do we need this sensor?
After one rotor movement, we need to turn a certain winding on to push the rotor again. A small amount of current runs through the Hall Strip at all times, so it determines the exact moment when we need to push the rotor. Due to this, the next commutation of the rotor can be initiated.
How do I choose an e-bike motor controller?
The following factors need to be considered when choosing the perfect e-bike motor controller:
1. Controller Voltage and Power
If you’re selecting a controller for a specific motor, check the controller's voltage and power. If you buy a non-programmable controller, ensure that the control voltage is the same as the motor voltage and the controller power is the same or slightly more than the motor power. For example, if the motor voltage is 24 volts, then the controller's voltage should be 24 volts.
If your controller is programmable, then this power can be limited if needed. The voltage of the controller should match the motor as well as the battery. With this consideration, you’ll reduce the heating of the controller, and its operation will be more stable, which increases the system's reliability.
2. Controller Current Rating
While selecting the controller, ensure that the controller’s current rating is lower than the battery’s output current. Generally, the maximum current for a 9-MOSFET controller is 25A, 18A for a 6-MOSFET controller, 40A for a 15-MOSFET controller, etc.
3. Phase and Battery Current
Most beginners can be confused between the phase current and the battery current. These are two different things. The phase current is connected to the motor. The phase current can be much greater than the battery current.
Let’s consider the example of a welding machine; it takes 10A from the network and gives all 100A at the output. The controller works on the same principle. It can take 30A from the battery and provide around 80A to the motor.
While choosing an E-bike motor controller for the motor, you need to check that the phase current of the controller and the motor current are matched. If the controller provides more current than the current motor capacity, it will heat up more and more.
When the motor overheats, the varnish coating on the wires begins to lose its properties. As a result, it creates a short circuit, and the motor starts to warm up rapidly and damage the windings.
Therefore, in normal e-bike motor controllers, the phase current of the controller must match the motor current. Then this configuration will not lead to the failure of individual components.
4. Controller Driving Type: Sine Wave or Square Wave Controller?
Both controllers differ in the phase voltage waveform. One generates a sinusoidal waveform, while the other generates a rectangular waveform.
Sine wave controllers are popular because of their lower noise production. As a result, it provides greater efficiency when going uphill or carrying a heavy load. Also, these controllers provide smoother and more predictable control over general operations. However, sine wave controllers consume much more power and will cost you more. In addition, they can operate with matched motors only.
People prefer square wave controllers because they are more affordable. They can function with different motors. These controllers provide higher efficiency during sudden braking or acceleration.
As compared to sine wave controllers, they produce high noise production and non-smooth or punched control. Also, square wave controllers are less motor-efficient when going uphill or carrying a heavy load.
5. Is it a Hall Sensor/Non-Hall Sensor Drive or a Dual-Mode Controller?
If your E-bike motor features a Hall sensor, the controller is supposed to be a Hall sensor or dual mode. The hall sensor in the motor senses the motor's rotation, and the controller generates the voltage depending on the sensor signals.
This motor controller is more stable and has lower power consumption with more starting torque.
Final Thoughts
In the market, there are different types of E-bike motor controllers available with various configurations. Therefore, kindly consider all the above parameters when choosing an e-bike motor controller.
Also, consider the required control functions, dimensions of the controller, etc. I hope this article helps you choose the perfect controller for your e-bike motor.







I just bought a Ho D50 scooter it was supposed to have no speed restriction on it but 25 kph top speed Not happy Manufacturer not very helpful though this is being advertised 30 kph on Alibaba.com
Is there any controller out there that will fit and to give me extra speed
Please reply
Nice information. Thank you ..