How Proximity Sensor Works?
In this article, we discuss about the proximity sensor in details such as what is proximity sensor, features, and how proximity sensor works.

Here, in this article, we discuss about the proximity sensor in details such as what is proximity sensor, features, and how proximity sensor works.
Before discussing in detail about the proximity sensors working, primarily, we will learn the features of the proximity sensor.
If you want to learn more about proximity sensor working check out the blog post on types of sensor, capacitive sensor, and
If you want to know more about different types of senors you can check the blog post on types of proximity sensors.
What is a Proximity Sensor?
A proximity sensor is a sensor which detects the presence of nearby objects without any physical contact.
This can be done using the electromagnetic field or electromagnetic radiation beam in which the field or return signal changes in the event of the presence of any object in its surrounding. This object sensed by the proximity sensor is termed as a target.
It is also known as a proximity switch. This definition given by the Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS) to all contactless detecting sensors.
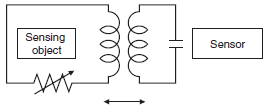
The sensing object and Sensor appears to be a transformer-like relationship.
 Proximity sensors have high reliability and long functional life because of the absence of mechanical parts and lack of physical contact.
Proximity sensors have high reliability and long functional life because of the absence of mechanical parts and lack of physical contact.
Proximity Sensors are available in models using high-frequency oscillation to detect ferrous and non-ferrous metal objects and in capacitive models to detect non-metal objects. This models are available with environment resistance, heat resistance, resistance to chemicals, and resistance to water.
Features of the Proximity Sensor
To understand what proximity sensor is all about, we’ll take a look on it's features. The followings are it's feature:
1. Contactless Sensing
Proximity Sensors detect an object without touching it and therefore, they do not cause abrasion or damage to the object. The devices such as limit switches detect an object by contacting it, but Proximity Sensors are able to detect the presence of the object electrically, without any touch.
2. Unaffected by Surface Condition
Proximity Sensors detect the physical changes of an object, so they are almost completely unaffected by the object's surface colour.
3. Suitability for a Wide Range of Applications
Proximity sensors are suitable for damp conditions and wide temperature range usage, unlike your traditional optical detection. They can be used in temperatures ranging from −40 to 200°C.
Proximity sensors are also applicable in phones like Android or IOS devices. It consists of simple IR technology that switches on/off the display accordingly to your usage. For example, it turns off your display when a phone call is ongoing such that you wouldn’t accidentally activate something while placing it near to your cheeks!
4. Longer Service Life
Since a proximity sensor uses semiconductor outputs so there are no moving parts dependent on the operating cycle. Thus, it's service life tends to be longer as compared to traditional sensors!
5. High-Speed Response
Compared to switches where contact is required for sensing, proximity sensors offer a higher-speed response rate.
6. Unlike optical detection methods, Proximity Sensors are suitable for use in locations where water or oil is used. Detection takes place with almost no effect from dirt, oil, or water on the object being detected. Models with fluororesin cases are also available for excellent chemical resistance
7. Unlike switches, which rely on physical contact, Proximity Sensors are affected by ambient temperatures, surrounding objects, and other Sensors. Both Inductive and Capacitive Proximity Sensors are affected by interaction with other Sensors. Because of this, care must be taken when installing them to prevent mutual interference. (Refer to the Precautions for Correct Use in the Safety Precautions for All Proximity Sensors.) Care must also be taken to prevent the effects of surrounding metallic objects on Inductive Proximity Sensors and to prevent the effects of all surrounding objects on Capacitive Proximity Sensors.
How does Proximity Sensor Works?
The proximity sensor circuit wiring is shown in the below figure. Depending on the transistor condition based on the absence of a target, proximity sensor outputs are considered as NC (normally closed) or NO (normally open).
If PNP output is low or off when the target is absent, then we can consider the device as normally opened. Similarly, if the PNP output is high or on when the target is absent, then we can consider the device as normally closed.
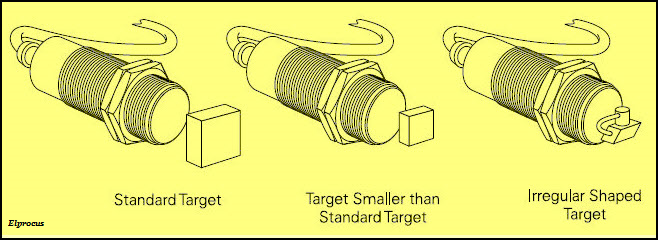
Proximity Sensor Circuit-Target Size
A standard target is a one which has a flat and smooth surface with a thickness of 1mm and made of mild steel. There are various grades in which steel is available and mild steel is made of a composition of carbon and iron (higher content).
The standard target with shielded sensors will be having sides that are equal to the diameter of sensing face. The sides of the target with unshielded sensors is equal to a greater one among the two, i.e., the diameter of the sensing face or thrice the rated operating range.
Even though the size of the target is greater than the standard target, there will be no change in the sensing range.
But, if the size of the target becomes less than the standard target or irregular, then the sensing distance will decrease. Thus, we can say that, as small as the size of the target, then the target must be moved closer to the sensing face to get detected.
Nowadays, the proximity sensors commonly found in smartphones. It uses the (IR) Infrared radiation which is invisible to the normal human eye.
An IR LED emits IR radiation which bounces off any nearby surface. The reflected rays are detected by an IR receiver which is next to the emitter. Based on the distance between the obstacle and the sensor, the intensity of light light falling on the receiver varies.
Hence, a high intensity light reflected back implies there is an obstacle or a surface nearby. These sensors are generally digital (or sometimes analog).
I hope this article helps you to understand the proximity sensor working principle, it's basics and it's features.