Difference Between Synchronous and Induction AC Motor
There are two types of AC Motors: Synchronous AC Motor and Induction Motor. Here’s what separates them in terms of excitation, starting mechanism, efficiency and applications.

The motor that converts the alternating current into mechanical power by using an electromagnetic induction phenomenon is called an AC Motor. Mainly an AC motor classified into two types. They are the synchronous AC motor and induction AC motor. In this blog, we are talking about the difference between Synchronous and Induction AC Motor with the help of various factors, like the type of excitation used for the machine. Speed of the motor, starting mechanism and operation, the efficiency of both the motors, their costs, usage, and applications.
1. Synchronous AC Motor
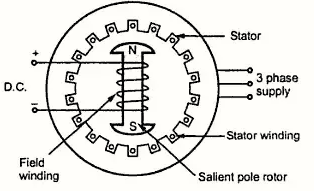
A motor that converts an AC electrical power into mechanical power and operates only at the synchronous speed is the synchronous motor.
In this motor, stator has axial slots which consist stator winding wound for a specific number of poles. Generally, a Salient Pole Rotor uses on which rotor winding is mounted. Rotor winding is fed with a DC supply with the help of slip rings. A rotor with permanent magnets can also be used.
When supply is given to synchronous motor, a revolving field is set up. This field tries to drag the rotor with it but because of rotor inertia it could not rotate. Hence,cit does not produce any starting torque. Thus, the synchronous motor is not a self-starting motor.
2. Induction or Asynchronous AC Motor
The machine which converts the AC electric power into mechanical power by using an electromagnetic induction phenomenon in called an induction motor. The induction motor classified into two types
- Single phase induction motor
- Three phase induction motors.
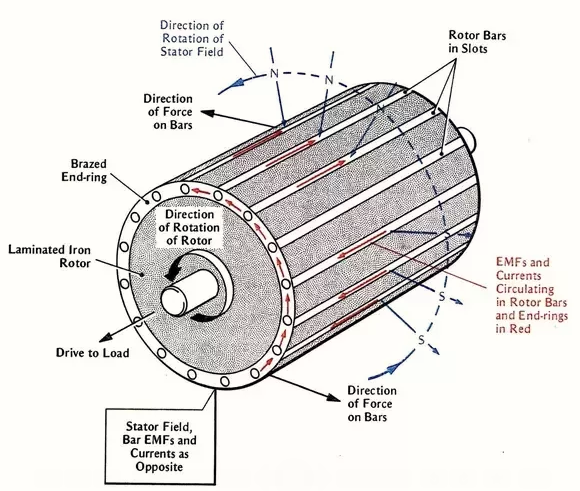
In an induction machine the armature winding serves as both the armature winding and field winding. When the stator windings connect to an AC supply, the flux produces in the air gap. The flux rotates at a fixed speed called synchronous speed. This rotating flux induces voltages in the stator and rotor winding. An Induction Motor is also known as Asynchronous Motor because it never runs at synchronous speed. i.e., Ns = 120f/P. The induction motor most widely uses motor in all domestic and commercial motor.
Here, stator winding is wound for a specific number of poles. A squirrel cage rotor or a wound rotor can be used. In squirrel cage rotor, the rotor bars are permanently short-circuited with end rings. In wound rotor, windings are also permanently short-circuited, hence no slip rings are required. If the rotor circuit closed, the current flows through the rotor winding and react with the rotating flux and it produces the torque. According with the torque, the speed will change.
RELATED BLOG POSTS ON AC MOTOR
Difference Between Synchronous and Induction AC Motor
Parameters |
Synchronous AC Motor |
Induction AC Motor |
| Supply System |
Its armature winding is energized from an AC source and its field winding from a DC source. |
Its stator winding is energized from an AC source. |
| Types of Excitation |
A synchronous motor is a doubly excited machine. |
An induction motor is a single excited machine. |
| Speed |
It always runs at synchronous speed. The speed is independent of load. |
If the load increased the speed of the induction motor decreases. It is always less than the synchronous speed. |
| Starting Mechanism |
It is not self starting. It has to be run up to synchronous speed by any means before it can be synchronized to AC supply. |
Induction motor has self starting torque. |
| Operation |
A synchronous motor operates with lagging and leading power by changing its excitation. |
An induction motor operates only at a lagging power factor. At high loads the power factor becomes very poor. |
| Usage |
It uses for power factor correction in addition to supplying torque to drive mechanical loads. |
An induction motor uses for driving mechanical loads only. |
| Efficiency |
It is more efficient than an induction motor of the same output and voltage rating. |
Its efficiency is lesser than that of the synchronous motor of the same output and the voltage rating. |
| Construction |
Construction is complicated |
Construction is simpler in case of cage rotor. |
| Cost |
A synchronous motor is costlier than an induction motor of the same output and voltage rating |
An induction motor is cheaper than the synchronous motor of the same output and voltage rating. |
We hope this article helps you to understand about the difference between Synchronous and Induction AC motor.
We at Robu.in hope that you found it interesting and that you will come back for more of our educational blogs.









Very nice tutorial even for a beginner.electrifying electric service to the modern world of scientific society.thank you . keep going.