Difference Between the L293D and L298N Motor Driver.
Know the differences between the L293D and the L298N motor drivers in terms of the power requirements, configurations and what an H-Bridge is? to Help yourself to choose best suited to your project.

In this blog post, we will explore the key differences between two popular motor driver ICs: L293D and L298N. Both these motor drivers have their unique features and applications. Understanding their dissimilarities will help you choose the right one for your specific motor control needs.
So let's dive in and explore the differences between L293D and L298N motor drivers.
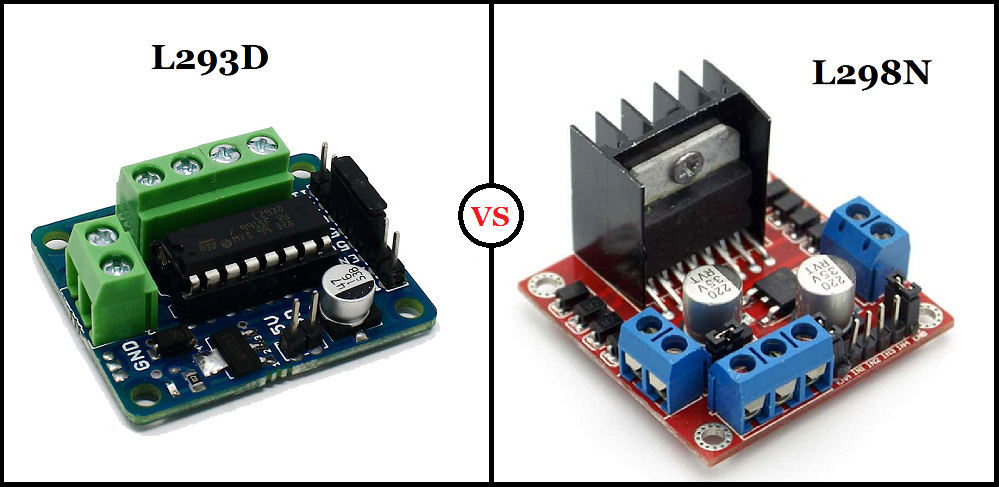
I know you landed here because you are curious to know the distinctions between the L293 and L298 motor drivers. But before delving into that, let's begin with some basic information about motor drivers, especially for beginners.
Motor driver circuits are necessary because regular DC motors require a current exceeding 250mA. Microcontroller chips like Atmega16/32 or 8051 cannot handle such high currents directly through their pinouts. Connecting motors directly to these chips would result in burnout due to the excessive current draw.
Furthermore, motors require a higher operating voltage for high-speed operation, which cannot be provided by the microcontroller alone. This is where motor driver circuits come into play. We cannot connect a motor directly to a microcontroller because the signals generated by the microcontroller (HIGH or LOW) have insufficient voltage to power the motor. Hence, we need a motor driver.
The widely used motor driver ICs are from the L293 and L298 series, including L293D, L293NE, and L298N. These ICs are designed to control two DC motors simultaneously and consist of H-bridge circuits. H-bridges are simple circuits for controlling low-current-rated motors. Now, let's delve into the main topic and discuss the differences between the L293 and L298 motor drivers, as well as their applications.
The basic difference between L293D and L298N Motor Driver:
-
Operating Voltage: The L293D operates within the range of 4.5V to 36V, while the L298N can handle up to 46V.
-
Current Handling: The L293D can draw a maximum of 600mA per channel, whereas the L298N can handle up to 2A per channel.
-
Driver Configuration: The L293D is a quadruple motor driver with independent input-output lines, using a half-H driver. In contrast, the L298N is a dual full-H driver, meaning it requires a full-H driver configuration and cannot be used independently as a half-H driver.
-
Output Current and Heat Dissipation: The L293D has an output current of 650mA per channel, while the L298N can handle up to 2A. The L298N motor drivers typically come with a heat sink due to the higher output current.
-
EMF Provision: The L293D has internal EMF protection, whereas the L298N requires external provision of EMF protection.
-
Suitable Applications: The L293D is suitable for motors with lower current requirements, such as BO motors, DC-geared motors up to 500 RPM, and small stepper motors with current draws up to 600mA. On the other hand, the L298N is ideal for high-torque and high-RPM motors, including Johnson motors and high-torque DC geared motors, thanks to its higher output current capability.
Understanding these distinctions will help you choose the right motor driver for your specific motor control needs.
Now you might have a question in your mind that what is H-Bridge? So, let's understand it in brief
H-BRIDGE is an electronic circuit that enables a voltage to be applied across a load in either direction.
It allows a circuit full control over a standard electric DC motor. That is, with an H-bridge, a microcontroller, logic chip, or remote control can electronically command the motor to go forward, reverse, brake, and coast.
H-bridges are available as integrated circuits or can be built from discrete components.
A “double pole double throw” relay can generally achieve the same electrical functionality as an H-bridge, but an H-bridge would be preferable where a smaller physical size is needed, high-speed switching, low driving voltage, or where the wearing out of mechanical parts is undesirable.
The expression “H-bridge” is determined from the ordinary graphical representation of such a circuit, which is fabricated with four switches, either robust state (eg, L293/ L298) or mechanical.

L298N is also available with an onboard Arduino Uno board to control the motor as per your project requirement. Hence you don’t need to do add any controller board and interfacing wiring with a separate Arduino board.
Talking about the cost comparison, there is no remarkable price difference in both drivers. Both drivers are available in the BRUSHED DC MOTOR DRIVER category at almost the same price under INR 150 to 200 bucks.
Additionally, here's a video to help you better understand the differences between the two motor drivers.
I hope this helped you to understand the difference between L293D and L298N Motor Driver. So depending on your project requirement choose the perfect motor driver.
That was the brief summary of both the L293D and L298N motor drivers, drop the comment below with your suggestion and feedback.






Thank you for the detailed clarification. It certainly helps in choosing the correct product for our applications.
Well explained, thank you for thorough comparison.
Nicely discussed.
I really appreciated your post on motor driver. It indeed added an extra knowledge about motor driver.
Thanks for that. Please move ahead and keep posting.