Working Principle of Capacitive Proximity Sensor
In this blog, we discuss about the capacitive proximity sensor working principle, their wide spread applications in industries and their use for commercial purposes.

In this blog, we will discuss about the capacitive proximity sensor working principle, their wide spread applications in industries and their use for commercial purposes.
What is Capacitive Proximity sensor?
Capacitive Proximity Sensors detect changes in the capacitance between the sensing object and the Sensor. As per the name, capacitive proximity sensors operate by noting a change in the capacitance read by the sensor.
The amount of capacitance varies depending on the size and distance of the sensing object. An ordinary Capacitive Proximity Sensor is similar to a capacitor with two parallel plates, where the capacity of the two plates detected.
One of the plates is the object being measured (with an imaginary ground), and the other is the Sensor’s sensing surface. It detectes the changes in the capacity generated between these two poles. The detection of the object depends on their dielectric constant, but they include resin and water in addition to metals.
MUST READ:
- How proximity sensor works?
- Different types of proximity sensor
- Working principle of Inductive Proximity Sensor
Working Principle of Capacitive Proximity Sensor
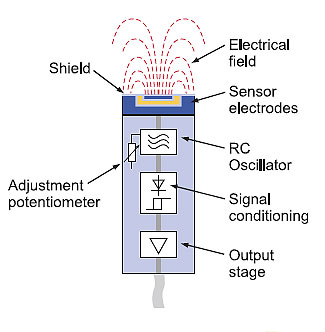
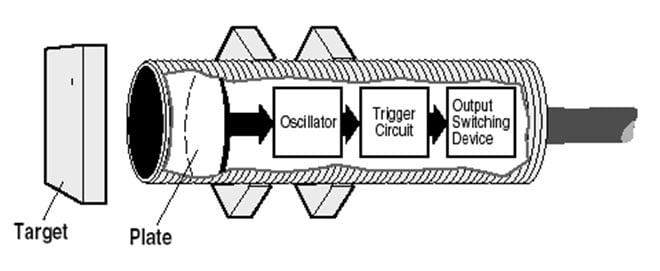
The capacitive proximity sensor consist a high-frequency oscillator along with a sensing surface formed by two metal electrodes. When an object comes near the sensing surface, it enters the electrostatic field of the electrodes and changes the capacitance of the oscillator.
As a result, the oscillator circuit starts oscillating and changes the output state of the sensor when it reaches certain amplitude. As the object moves away from the sensor, the oscillator’s amplitude decreases, switching the sensor back to its initial state.
A typical sensing range for capacitive proximity sensors is from a few millimeters up to about 1 inch. (or 25 mm), and some sensors have an extended range up to 2 inch. Where capacitive sensors really excel, however, is in applications where they must detect objects through some kind of material such as a bag, bin, or box. They can tune out non-metallic containers and can be tuned or set to detect different levels of liquids or solid materials.
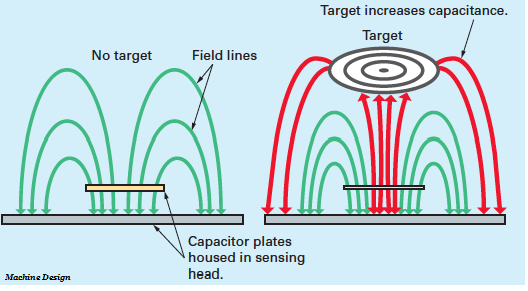
The capacitive proximity sensor detects the larger dielectric constant of a target easilty. This makes possible the detection of materials inside nonmetallic containers because the liquid has a much higher dielectric constant than the container, which gives the sensor ability to see through the container and detect the liquid.
For best operation, they should use in an environment with relatively constant temperature and humidity.
When dealing with non-conductive targets there are three factors that determine the sensing distance.
- The size of the active surface of the sensor – the larger the sensing face the longer the sensing distance
- The capacitive material properties of the target object, also referred to as the dielectric constant – the higher the constant the longer the sensing distance
- The surface area of the target object to be sensed – the larger the surface area the longer the sensing distance
Other factors that have minimal effect on the sensing distance
- Temperature
- Speed of the target object
The point at which the proximity sensor recognizes an incoming target is the operating point. The point at which an outgoing target causes the device to switch back to its normal state is the release point. The area between operating and release points is the hysteresis zone.
Most proximity sensors are equip with an LED status indicator to verify the output switching action.
The difference between Inductive and Capacitive Proximity Sensor:
Inductive sensors use a magnetic field to detect objects. Capacitive sensors use an electric field. In order to be sense by an inductive sensor an object must be conductive. This limits suitable targets to metal objects (for the most part). In order to be sense by a capacitive sensor the target doesn’t need to be conductive.
A capacitive sensor will react to an object acting as a dielectric material as well as a conductive object. This makes metal and non-metal objects suitable targets.
Advantages of Capacitive proximity sensors
- Contactless detection
- A wide array of materials can detect
- Able to detect objects through non-metallic walls with its wide sensitivity band
- Well-suited to be used in an industrial environment
- Contains potentiometer that allows users to adjust sensor sensitivity, such that only wanted objects will be sensed
- No moving parts, ensuring a longer service life
Disadvantages of Capacitive proximity sensors
- Relative low range, though incremental increase from inductive sensors
- Higher price as compared to inductive sensors
Capacitive sensing technology uses in other sensing technologies such as:
- flow
- pressure
- liquid level
- spacing
- thickness
- ice detection
- shaft angle or linear position
- dimmer switches
- key switches
- x-y tablet
- accelerometers
Hope this article will help you to understand the complete Capacitive proximity sensor working principle.